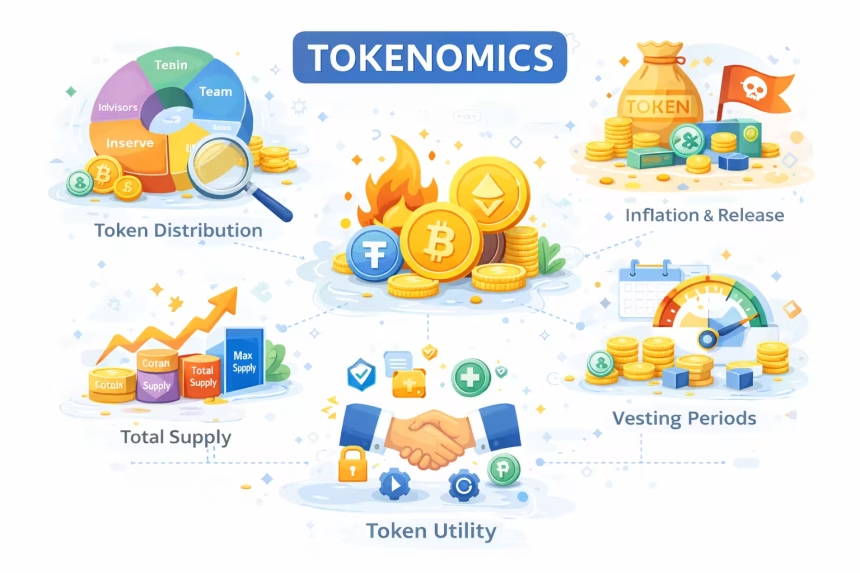
Tokenomics (a combination of token and economics) refers to the economic design and structure of a cryptocurrency or blockchain token. It defines how a token is created, distributed, used, and managed within an ecosystem.
In simple terms, tokenomics explains:
- How many tokens exist
- Who gets them
- How they are used
- How their value is maintained or increased over time
Strong tokenomics can make a crypto project sustainable, while poor tokenomics often leads to price crashes and loss of investor trust.
Why Tokenomics Is Important in Crypto
Tokenomics plays a critical role in determining the long-term success of a cryptocurrency.
Good tokenomics helps:
- Maintain scarcity and demand
- Prevent excessive inflation
- Align incentives between users, developers, and investors
- Support healthy price growth
Bad tokenomics can result in:
- Rapid token dumping
- Centralized control
- Unstable prices
- Project failure
This is why experienced investors always analyze tokenomics before investing.
Key Components of Tokenomics
1. Token Supply
Token supply defines how many tokens exist or will exist.
Types of Token Supply:
- Maximum Supply: The absolute cap (e.g., Bitcoin’s 21 million)
- Total Supply: Tokens created minus burned tokens
- Circulating Supply: Tokens currently available in the market
Example:
Bitcoin’s fixed supply creates scarcity, which is one reason for its high value.
2. Token Distribution
Token distribution shows how tokens are allocated among different stakeholders.
Common allocation includes:
- Public investors
- Founders and team
- Advisors
- Community rewards
- Ecosystem development
- Liquidity pools
Red Flag:
If founders hold too many tokens, it increases the risk of dumping.
3. Token Utility (Use Case)
Utility defines what the token is used for.
Common utilities include:
- Paying transaction fees
- Governance voting
- Staking and rewards
- Accessing platform features
- Incentives for users and validators
Tokens with real utility tend to perform better long term.
4. Token Burning
Token burning permanently removes tokens from circulation, reducing supply.
Why projects burn tokens:
- Reduce inflation
- Increase scarcity
- Support price stability
- Reward long-term holders
Example:
Ethereum burns a portion of transaction fees, reducing supply over time.
5. Inflation and Emission Rate
This defines how new tokens are released.
- High inflation = downward price pressure
- Controlled emission = healthier ecosystem
Projects often use:
- Block rewards
- Staking rewards
- Gradual unlock schedules
6. Vesting and Lock-Up Periods
Vesting ensures tokens are released gradually over time, especially for founders and early investors.
Benefits:
- Prevents sudden price crashes
- Aligns long-term commitment
- Builds investor confidence
Types of Tokens Based on Tokenomics
1. Utility Tokens
Used within a platform (e.g., paying fees, accessing services)
2. Governance Tokens
Allow holders to vote on protocol decisions (common in DeFi)
3. Security Tokens
Represent ownership or financial assets (regulated)
4. Reward Tokens
Earned through staking, farming, or participation
Tokenomics in DeFi Projects
In DeFi, tokenomics is even more important because tokens often control:
- Protocol governance
- Liquidity incentives
- Yield farming rewards
- Platform sustainability
Poor DeFi tokenomics often leads to:
- High APYs followed by collapse
- Liquidity draining
- Short-term hype projects
How to Analyze Tokenomics Before Investing
Before investing, check:
- Total and circulating supply
- Token distribution fairness
- Real utility of the token
- Inflation or burn mechanisms
- Vesting schedules
- Governance structure
Always review:
- Whitepaper
- Tokenomics chart
- On-chain data
Common Tokenomics Red Flags
- Unlimited supply with no burn
- Heavy founder allocation
- No real use case
- Aggressive emission rate
- No vesting for early investors
Real-World Tokenomics Example
Bitcoin (BTC):
- Fixed supply (21 million)
- Halving reduces inflation
- No central authority
- Strong scarcity model
Ethereum (ETH):
- Fee burning mechanism
- Utility for gas fees
- Strong demand from DeFi and NFTs
Tokenomics vs Market Price
Tokenomics does not guarantee price increase, but it creates the foundation for sustainable growth.
Price depends on:
- Demand
- Market sentiment
- Adoption
- Utility
- Tokenomics design
Strong tokenomics + real adoption = long-term value.
Final Thoughts: Why Tokenomics Matters
Tokenomics is the backbone of every crypto project. It determines whether a token is built for:
- Long-term growth
- Fair participation
- Sustainable economics
Understanding tokenomics helps you:
- Avoid scams
- Make smarter investments
- Identify strong projects early
Before buying any crypto, always ask:
Does this token have solid tokenomics?